The Tools Behind FOOH Ads
Learn how tools like motion graphics, visual effects, and audio design come together to create the magic of FOOH ads in modern marketing.
Visual culture is more intense than at any time in history. With audiences constantly exposed to countless ads and visual stimuli every day, brands need to think outside the box to capture attention. Enter Fake Out Of Home (FOOH) advertising – a game-changer in marketing that blends real-world footage with photorealistic CGI elements to create eye-catching, share-worthy content that demands a second look.
This blog series takes you behind the scenes of what it really takes to plan and execute a successful CGI ad production.
We’ll explore the essential tools and techniques that bring groundbreaking FOOH ads to life—from software and equipment to digital solutions.
Each article breaks down a specific stage of the creative process, spotlighting the tools that streamline workflows, stretch creative limits, and deliver high-impact visuals that work across platforms.
Whether you’re a seasoned production or marketing professional, a 3D artist, or just getting into VFX and fake out of home advertising, this series will equip you with valuable insights into the ever-evolving world of FOOH ads and how augmented reality is shaping the future of advertising.
Sign up for our newsletter to get the latest on new blog posts and exciting updates on Fake Out Of Home trends – delivered straight to your inbox!
The Key Steps behind FOOH ads
1. Ideation and Concept Development
The first step in creating FOOH ads is the ideation phase, where the creative concept is developed. This process involves brainstorming ideas, understanding the target audience, and defining the core message of the advertisement.
Here it’s essential to visualize the concept, either through sketches, mood boards, or rough drafts, to establish a clear direction for the project. This phase sets the foundation for the entire production and ensures that all team members are aligned with the creative vision.
Want to know more about the best tricks and tools for concept development? Discover them in the first installment of our blog series: The Tools Behind FOOH Part I: Ideation and Concept Development
2. Pre-Production Planning
Pre-production is the planning phase where the concept starts to take shape into a structured production plan. This includes:
- Creating detailed storyboards and shot lists.
- Planning the logistics for the shoot.
- Making key decisions regarding scenes, camera angles, lighting, and composition.
- Securing necessary permits to ensure all legal and location requirements are met.
This phase ensures all technical and creative elements are mapped out, minimizing surprises during filming. It also involves coordinating resources, such as casting, locations, and equipment.
3. Shooting and Capturing Footage
With planning complete, the filming process begins. During shooting, the director and crew focus on capturing high-quality footage, ensuring that the planned shots are executed as intended.
This stage involves directing actors and positioning the camera to achieve the desired visual style. Attention is also given to ensuring the right environment is set up for optimal footage quality.
4. Camera Tracking
After filming, camera tracking is crucial for integrating digital elements into live-action footage. This process involves:
- Analyzing the camera’s movement throughout the scene.
- Replicating that movement in a 3D space.
This ensures that any added digital effects or CGI objects align properly with the live-action footage, creating a seamless integration between real-world and virtual elements.
5. Rotoscoping and Matte Creation
Rotoscoping is the process of isolating specific elements within a scene, often to separate the foreground from the background. This technique is necessary when digital effects or new elements need to be inserted into a shot without disturbing the original footage.
Rotoscoping involves manually or automatically creating mattes (or masks) that define the boundaries of these elements, such as actors or objects in motion. This step allows for precise control over which areas of the image are affected by visual effects and which are left untouched, ensuring clean and accurate compositing later in the process.
6. Creating Visual Effects (VFX)
Now this is where the magic happens, literally: Visual effects are the heart of FOOH ads, adding elements that cameras simply can’t capture.
Whether it’s subtle enhancements like color grading or jaw-dropping CGI like explosions, animated characters, or surreal environments, VFX takes creativity to the next level.
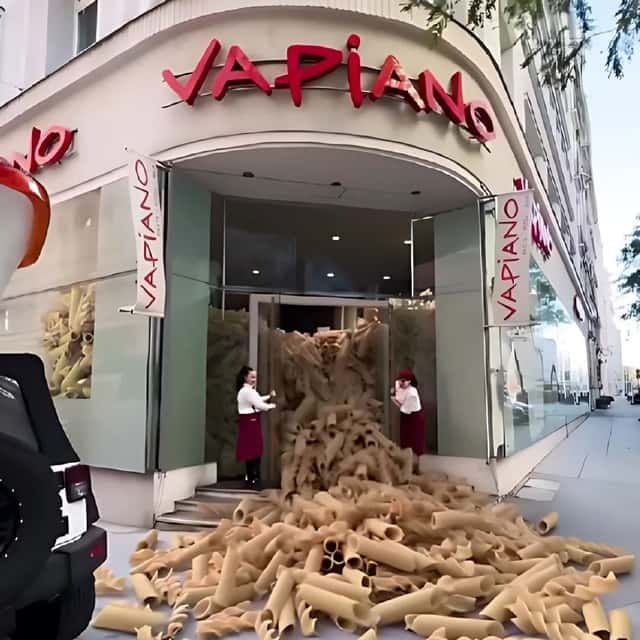

VFX artists use 3D modeling and animation techniques to create objects or scenes that interact with live-action footage in a realistic way.
This stage can involve intricate particle systems, simulations of natural phenomena, and the creation of complex textures to ensure the added elements appear lifelike and integrated into the real-world footage.
7. Compositing and Video Editing
Compositing is the final step where all the visual elements – live-action footage, VFX, animations, and graphics – are combined to create the final image. This stage ensures that all digital elements are seamlessly integrated with the real footage, adjusting lighting, shadows, and reflections to match the scene’s environment.
Once compositing is complete, the footage moves into video editing, where the overall pacing, structure, and flow of the ad are refined. This includes cutting scenes, adjusting timing, and syncing audio with video. The final step in video editing involves color correction, sound design, and any necessary adjustments to ensure the ad is polished and ready for distribution.
How The Right Tools Drive Your CGI Ads Impact
FOOH ads are a powerful fusion of creativity and technology, demanding the use of cutting-edge tools and expert techniques.
Mastering the tools outlined in this series enables professionals to create high-quality ads that not only captivate audiences but also leave a lasting impression in a highly competitive market.
Success in FOOH ads lies in seamlessly integrating the right technology at each production stage, from concept to final edit. By leveraging these tools effectively, you can transform bold ideas into stunning visual experiences that define the future of advertising.
FAQ: Softwares for VFX & FOOH Ads
1. What is VFX in advertising?
Visual Effects (VFX) in advertising refers to the use of computer-generated imagery (CGI), motion graphics, and special effects to create visuals that wouldn’t be possible with traditional filming methods. In Fake Out of Home or FOOH ads, VFX is used to superimpose realistic digital advertisements into real-world environments, making them appear as though they exist in physical spaces.
2. Which are the top software tools for FOOH ads?
The most widely used software tools for VFX in FOOH ads include:
- Adobe After Effects: Excellent for motion tracking and compositing.
- Cinema 4D: Best for 3D modeling, animation, and integration with After Effects.
- Unreal Engine: A leader in real-time rendering for immersive visual experiences.
- Blender: Free, open-source, and versatile for 3D design and animation.
- Nuke: Industry-standard for advanced compositing and post-production.
3. Why do SFX matter in FOOH ads?
In fake out-of-home advertising, sound effects (SFX) matter because they make the experience feel more immersive and convincing. By incorporating authentic sounds, such as ambient street noises, SFX amplify the realism of FOOH ads, making it feel less fabricated and more authentic.
4. Are there free softwares available for creating FOOH campaigns?
Yes, free tools like Blender and DaVinci Resolve offer powerful features for creating VFX and FOOH campaigns, making them great options for small teams or beginners.
5. What is the difference between editing tools like Adobe After Effects and Nuke?
After Effects is great for simpler, quick ad placements using basic motion tracking and compositing. It’s user-friendly but less precise for photorealism. Nuke, on the other hand, excels in high-quality, complex integrations with advanced 3D tracking, lighting, and environmental realism, making it ideal for professional VFX.



